Catheter ablation of arrhythmias in heart failure
What does it do?
Episodes of rapid heart beat (supra-ventricular or ventricular arrhythmias) are quite common in the natural history of chronic heart failure, and are frequently associated with a worsening of symptoms that may require hospitalisation. Medical therapy of heart failure decreases the frequency of such complications but often fails to eliminate them. When the risk of ventricular arrhythmias is high, an implantable cardiac defibrillator (ICD) can be implanted to treat these serious arrhythmias that can lead to worsening of symptoms or sudden death. However an ICD does not decrease the incidence of arrhythmias and the specific medications which might reduce these rhythm disturbances may be contra-indicated in heart failure.
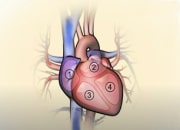
Catheter ablation is at this time the most efficient therapy to reduce arrhythmia. In heart failure, cellular changes may modify the pattern of electrical activation. Thus, some parts of the heart may activate spontaneously (premature ventricular contraction) or be part of an electrical loop, re-entry system that may perpetuate and lead to persistent rapid heart rate. Catheter ablation aims to create superficial scars with the use of a radiofrequency catheter or cold application with a cryoballoon, in the electrical conduction system of the heart to eliminate the area that triggers the arrhythmia. Similarly, catheter ablation may be effective in eliminating or reducing the frequency of atrial fibrillation.
Catheter ablation is used for 2 main reasons
- To decrease episodes of rapid heart beat induced by supra-ventricular (atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation) or ventricular arrhythmias.
- To decrease the risk of sudden cardiac death (ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation).
Catheter ablation has been used for several decades and has been shown to reduce arrhythmias efficiently and to improve cardiac function in specific cases. Technological improvement of catheter ablation permits treatment of more complex arrhythmia in all cardiac cavities.
Catheter ablation is made up of 3 parts
- A diagnostic catheter to localize the electrical signals and map out the pattern of conduction.
- An ablation catheter to generate scar with different types of energy (radiofrequency, cryotherapy).
- System to localize the position of the catheter in the heart (fluoroscopy or three dimensional system).
How is it performed?
Catheter introduction into the heart is performed through the femoral vein with local anaesthesia. The first part of the procedure consists in studying and localizing the origin of the arrhythmia. Then, the catheter ablation requires a general anaesthesia or sedation. Several applications of energy are performed to create the scar in the appropriate areas. The success of the procedure is regularly tested to demonstrate that the abnormal electrical conduction cannot be triggered which defines the end of the procedure.
After the procedure
After the procedure, you will stay for 24-48 h in a cardiology ward to monitor the eventual recurrence of arrhythmia. Depending on the arrhythmia and the procedure you may expect to be asked to rest slightly for a few days.
Potential rare, but possible adverse events may include: bleeding, a need for cardiac surgery, embolism, arrhythmia or atrio-ventricular block requiring a pacemaker.
Recurrences of arrhythmia can be observed within the first months due to some changes during the healing process. The procedure of catheter ablation can be performed several times to treat recurrence or other arrhythmias that may develop.
Please speak to your Doctor or Nurse for more information.